- Mar 16, 2025
Context-Aware and High-Quality Cluster Summarization
- Chaomei Chen
- 22 comments
A well-structured literature review is essential for making sense of a knowledge domain, whether it spans a specific research topic, an entire field, or multiple interrelated disciplines. A common approach involves identifying major concentrations of scholarly publications—clusters that emerge based on semantic, linguistic, ontological, and historical similarities.
However, a critical and cognitively demanding challenge remains: how do we synthesize these computationally identified clusters into meaningful insights? Understanding what is going on at a higher level requires an effective balance between automation and expert-level synthesis.
Updated: 7/22/2025
AI-Assisted Cluster Summarization in CiteSpace
CiteSpace has long supported cluster labeling and summarization, leveraging advances in Natural Language Processing (NLP) and, more recently, Large Language Models (LLMs). (See my previous blogs for earlier discussions on this topic.)
In a concept-proving experimental release of CiteSpace on March 12, 2025, we are making a significant step forward in improving AI-assisted cluster synthesis. The goal is to enhance the quality of summaries so they more closely resemble a well-written scholarly review article by a domain expert.
Basic Steps
Generate a network in CiteSpace. I highly recommend a network of co-cited references, aka a document co-citation analysis, for its values as concept symbols and specific contributions in a broad context.
Use the All-in-One function to divide the network into clusters and label clusters with CiteSpace built-in labeling methods.
Double check settings for GPT-labeling and summarization such as the language for the output and any adjustments of the default settings for your specific situation such as the API rate limit. These options are under the menu Clusters > GPT.
Start the process with the GPT button on the tool bar. It has a light green background.
It usually takes a few seconds to complete, but we may feel much longer than it is. You can check its status in the command line console. You will see something like the following. When you see the line completed, then it is done.

Now the cluster labels in the display should be already switched to the labels that the GPT came up with. You can re-run the GPT function but choose to use existing labels to display labels stored from the most recent run. If you need to refresh the labels altogether, you can choose the other option.
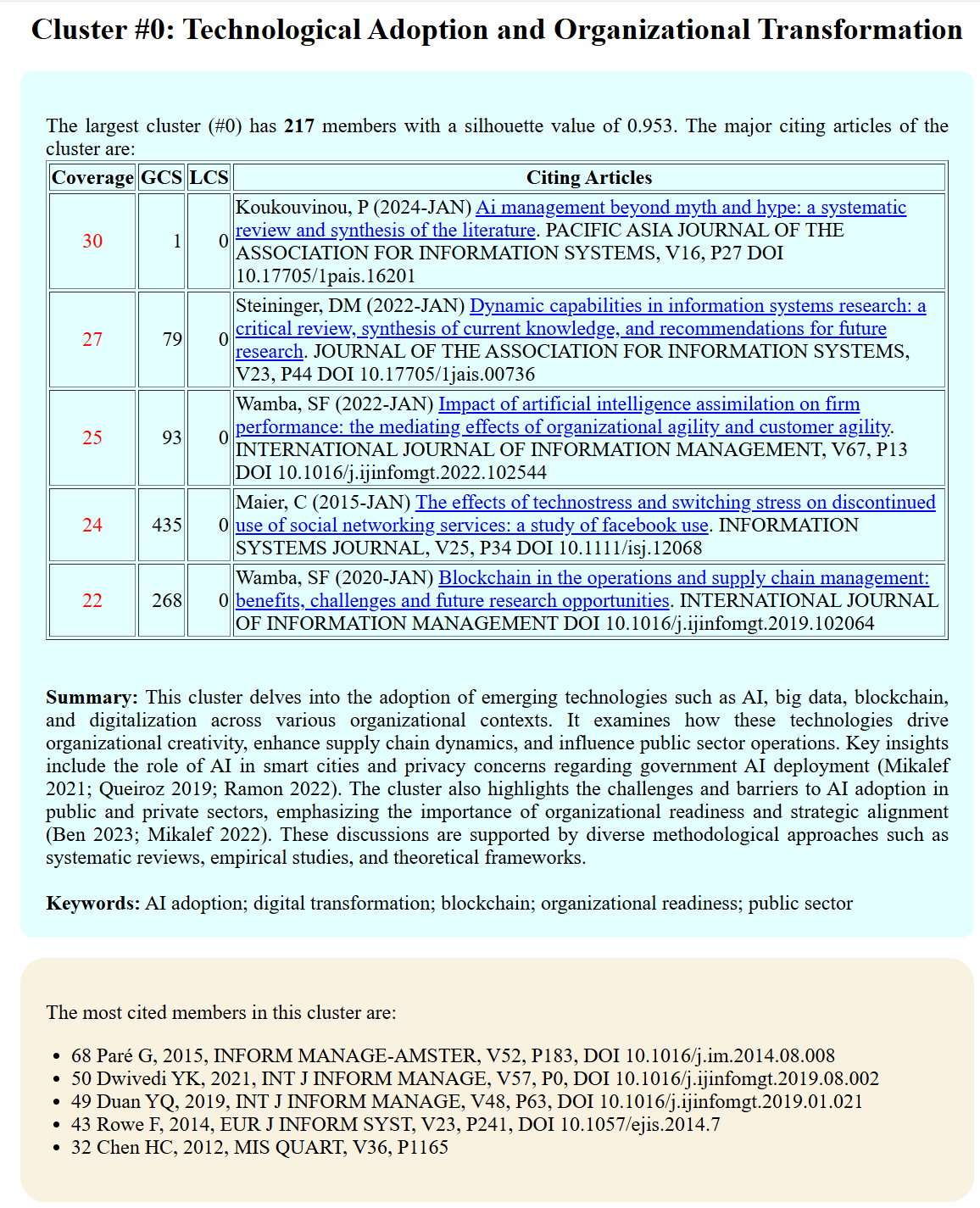
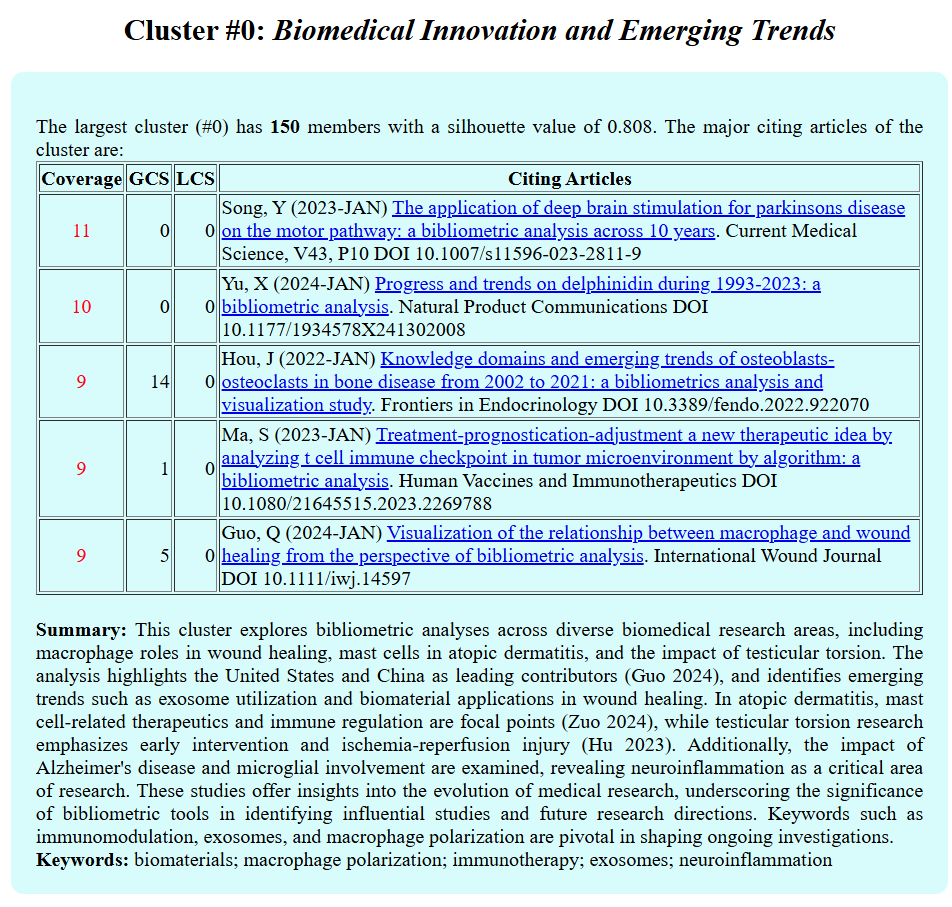
Follow the menu Summary > Summary Report, you will see the summaries among other information. The summary of each cluster consists a few parts. First, it shows a table of 5 citing articles to the cluster that have the highest coverage in terms of the number of members in the cluster they cite. In this illustrative example, the first citing article cited 30 members of the cluster out of a total of 217.
The actual summary follows the citing article table. Then, a list of keywords. Finally, a table of cited articles.
What's Old
The previous implementation of cluster labeling and summarization using LLMs like GPT-4 had a notable limitation:
Cluster labels may overlap or overly broad because they were generated independently for each cluster, leading to similar names across distinct clusters.
Summaries lacked meaningful contextualization, making it difficult to understand how key themes connected to specific scholarly works.
To address this, we have integrated GPT-4o via OpenAI’s API into CiteSpace. Looking ahead, I anticipate that future versions of CiteSpace will offer additional cost-efficient, high-quality AI models for enhanced literature review support.
What's New
1. Unique and Context-Aware Cluster Labels
The new implementation ensures that each cluster label is unique and meaningful by considering all clusters simultaneously when generating labels. This eliminates overlapping or overly generic labels, resulting in a clearer and more distinct taxonomy of research themes.
2. Scholarly Citation-Integrated Summaries
The enhanced cluster summarization process incorporates citations directly into the summary.
Key articles cited within the dataset are referenced using ALA-style in-text citations, providing direct connections between summarization points and supporting literature.
This context-aware synthesis follows the way a human expert would construct a review, ensuring that each summary is both data-driven and interpretatively rich.
Example: Terrorism Research Project
To illustrate, the built-in Terrorism Research project in CiteSpace now generates:
Distinct cluster labels—each capturing a unique research theme.
Summaries enriched with scholarly citations, ensuring precise and well-supported thematic synthesis.
A list of keywords suggested by GPT-4o, further refining the conceptual structure of each cluster.
This new approach significantly enhances the readability, coherence, and usability of cluster summaries, enabling researchers to quickly grasp the landscape of their field and identify key works for further reading.
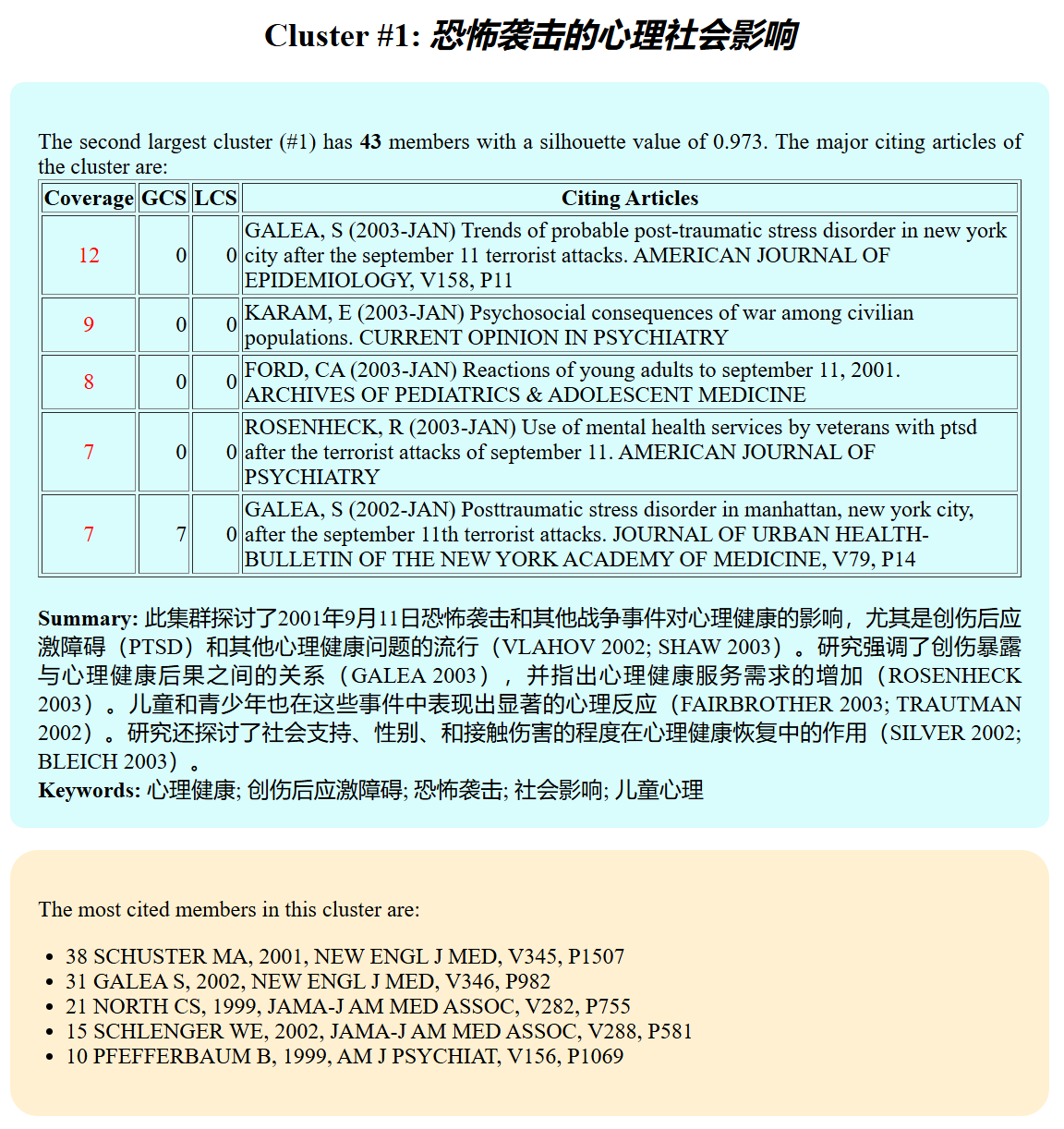
The new version of a cluster summary highlights key themes along with citations to specific and highly cited citing articles (wordy but precise) to support the summarization points. These cited articles provide convenient stepping stones for further and deeper exploration of the cluster.
A list of keywords is also provided by gtp-4o.

Future Developments
While GPT-4o has significantly improved cluster summarization, there are still factors to consider:
Cost Efficiency: The overall computational cost is influenced by the number of tokens processed.
Scalability: Large-scale analyses with many large clusters require careful optimization to balance detail vs. cost.
Expanded Model Support: Future versions of CiteSpace may integrate additional LLM options to provide more flexibility in balancing cost, accuracy, and detail level.
My long-term vision is to enable AI-assisted literature reviews to match the quality of expert-written synthesis, helping researchers work more efficiently and gain deeper insights.
Try it out and share your experience!
22 comments

Hi, i used citespace for an analysis back in 2017 (Niewiarowski, Peter H., Alyssa Y. Stark, and Ali Dhinojwala. "A bibliometric analysis of gecko adhesion: a view of its origins and current directions." Bio-inspired structured adhesives: biological prototypes, fabrication, tribological properties, contact mechanics, and novel concepts (2017): 1-19.) and i have returned to this program for another project....i can't get the chatgpt summaries to work, and despite working with the AI citespace agent, it is not resolved...so i have not been able to figure what to do next. One simple question answered might help: do i need a monthly subscription to openAI...or just an account with a balance with free access? BTW....i have tried this with the terrorism data set to test functionality and it does not work

Hi Peter, Thank you for your interest. The GPT-augmented summarization feature requires that you have an API account with OpenAI. Note that the API account is different from a ChatGPT plus account. Once you get your API key from OpenAI, you can set up some environment variables with your API key. Then you should be able to use the summarization feature. I will explore more options further down the road. At this point, the results are pleasant and encouraging.

Thank you....i did not describe the issue clearly. I did buy and receive an API key....but I have found no way to successfully execute the gpt option without an error 429....with citespace hanging up there. The tokens requested in the error message show to be below the limit. I started with the terror demo data set so I could try and troubleshoot...and have used the citespace chatgpt agent for help....so far nothing has worked

error 429 is most likely to do with your rate limit, which is apparently lower than the ones I tested with. Please check your rate limit in your OpenAI account and let me know. I will make sure to take that into account.

i can't get this to work. i created a small dataset ~800 records. ran all in one, selected chatgpt labeling...it ran 15 clusters and submitted 25K tokens...the chatgpt4o limit is 30K...so it is under. i can't figure out how to make this work. i tried to reduce the number of clusters, but that appears to just be about visualization, not clusters submitted...don't know where or if there is an option to limit which clusters are submitted for the chatgpt labeling. what is the second most common source of problems associated with the error 429....? can you help me get this to work?

Try the new release (4/8/2025). It has a lower default rate limit and the user can set it to match the rate limit of their own account accordingly.

ok, i will give it a shot. thanks

struggling...for the life of me, i just can't get this to work...I downloaded the new version, installed it. I set the rpm to match my account (500), ran the terrorism sample data...did all in one, then selected to show the top 3 clusters...that worked...it gets timeout with anything higher than 3. I tried my own data set...could only run the chatgpt on a single cluster (of 15). Thought that if i just did them one by one, maybe that was a work around. went to cluster menu and showed cluster by ID...but the gpt labeling always goes to the one largest cluster. Is there a way to step through the clusters by telling chatgpt which to do per run? thanks

It would be indeed challenging to run this function with 500 rpm. On the other hand, your account's rpm will increase as your mileage/usage grows. Summarizing multiple clusters altogether is intentional so that the GPT model can take all thematic variations into consideration and better characterize each cluster in the same broader context. I will bear in mind the need to work with the rpm constraints. In the meantime, you may try various configurations of your project and work with a smaller network to begin with, for example, project properties: LRF=2; LBY=5; e=3.0; g-index (k=25). I hope this helps.

thanks. As a work around, can you tell me if the following coarse algorithm might capture the essence of how you have implemented the chatgpt routine for summarizing cluster 'meaning?' If I took a sample of the 5 citing articles (for my settings) and 5 most cited papers from the narrative summary report and submitted them to chatgpt manually one cluster at a time asking for a summary of the combined abstracts....?

The quality may not be as good as you might expect. If you like, I'd be happy to generate some summaries for you so that you can start to analyze your dataset. Let me know at info.citespace@gmail.com.

that's extremely generous...will do. thank you

before i try and send you some cluster info, can you tell me how to limit (show?) subsets of clusters from a network such that i can generate gpt summaries on subsets which will not lead to the rate limitation? i ran the gpt summary on the 5 largest clusters with 10 instead of 50 citations (the default) and it worked. But citespace 101 chatgpt leads me to believe that those summaries are saved and i can select another subset and run seperately until i run through all the groups. so far i have not been able to figure that out. BTW, i purchased a personal plus plan to reduce the throttling of my requests.

also, do you want feedback on the citespace 101 chatgpt agent? I have spent a lot of time using it...very little has been directly useful...i can explain what i mean if you want or if there is another place you are collecting feedback on that

Note that if you set the rate limit (rpm) in CiteSpace to match the rate limit of your API account, you should be able to handle more tokens, i.e., more clusters with more details. Bear in mind the significant advantage of summarizing all clusters at the same time. You will get better differentiated cluster labels and summaries than get it done a subset at a time. While the summaries are indeed saved under the clusters folder in a JSON file named clusters_summaries.json, currently CiteSpace processes all the clusters at the same time for the above reason. You are certainly welcome to email me your feedback on the citespace 101 GPT.

I wonder if you can give me a bit more guidance. I set my rate limit in citespace to 20 which is much lower than my account rpm (500), but it seems i run out of tokens...is there a token limit (my account is at 30K) setting in citespace that would help me achieve the ideal approach you noted above? Also, i though you may have told me that it would be possible to have citespace call on a different model...the table below suggests that several alternatives could get me around the rate limits, but i can't find the info on how to have citespace specify a different model...there is only one option in my release 4o even though the menu suggests that a different model could be selected. thanks


陈教授,我使用了最新版的gpt生成聚类标签功能,对一个很小的网络,k=3,lby=5,1年时间切片,将rpm调整为10仍然报429,但是使用6.3.r3版本的gpt功能则可以正常生成标签,甚至对大得多的网络都可以成功,这是为什么呢,如何才能正常使用最新版的gpt生成聚类标签功能呢?

hello, i translated your message above and am wondering about the characteristics of the larger network you referenced working with the earlier version of citespace...my network which i can't process beyond 5 of the 13 clusters contains approximately 1300 papers WOS, i set rpm to 20 and top k citers per cluster to 10 (instead of default 50) and i get error 429. I wonder if the earlier version works because the gpt model is earlier and has a much higher token limit?

Peter and Jianhao,
I appreciate your feedback. This will be taken into account in future updates.
CiteSpace 6.4.R2 currently uses gpt-4o. Other models will be added in future releases. Based on the tests so far gpt-4o generated results have the highest quality. The general idea here is to support the high-quality results first and then reduce the cost.
According to the chart below, if you are using Tier 1, you would have a TPM limit of 30,000. CiteSpace will make 3 attempts to reduce the overall tokens. It may eventually fail if it can't make it through. To deal with these constraints, you can try and find a K of the top K citers per cluster that works for you. You did mention this approach worked for you for a small K. The good news is as you keep using the API, you would move up to higher Tiers.
Alternatively, you may certainly try previous version of the GPT function, e.g., in 6.3.R3, but check by blogs for details. The difference between the old and the new versions is significant:
old version: label and summarize one cluster at a time
pros: fast, fewer constraints on API connection
cons: quality is not as good as the new version
new version: label and summarize all clusters together
pros: high-quality results, including specific citations in cluster summaries.
cons: higher demands of Tier-specific constraints such as RPM and TPM.
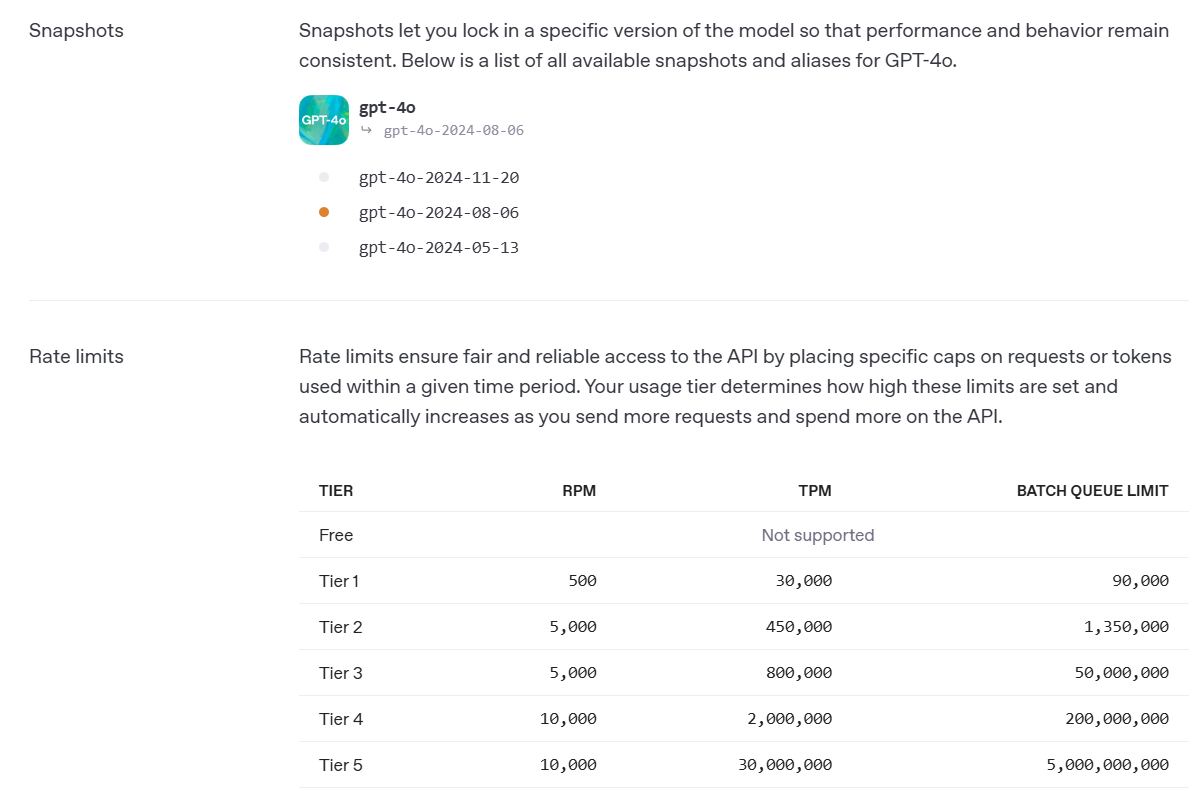

Hello Peter, when I was using version 6.3. r3, for a dataset of over 3000 articles, setting k to 100 resulted in 30 clusters, and processing the top 50 articles in each cluster, the GPT label generation function could still run normally. According to Professor Chen's explanation and my understanding, the earlier versions summarized each cluster one by one, so they were less sensitive to tpm and rpm restrictions. However, the results obtained may not be as expected. For example, I found that the same labels and similar summaries are generated for different clusters, but the new version's feature is to simultaneously summarize all clusters and consider their connections, generating higher quality labels and summaries. At the same time, the result is that it is easier to achieve restrictions. A better solution is to... Improve the usage level of GPT API.

I was finally able to get labels and summaries for all 13 clusters by throttling the number of top citers per cluster down to 3 by the time i got to all thirteen clusters, and leaving rpm at 10...crashing seemed to be more sensitive to the number of top citers per cluster to include, than to the rpm...it would crash when " input" reached about 22000...


Thanks for the update. You can enter 500 rpm for Tier 1 or 5,000 for Tier 2 according to the chart above. 10 rpm is an overkill. You can try it and see if it gets faster.